A Logical Model is the way the data in Salted CX are organized, making them easy to use for a wide range of analytical needs. The Logical Model is designed to be easy to understand for people without deep technical knowledge. Understanding the logical model is helpful for creating custom metrics, building reports, and designing dashboards.
Data Sets
Data sets represent different kinds of items stored in the logical model. Salted CX uses a limited set of data sets that enable users to quickly navigate in it.
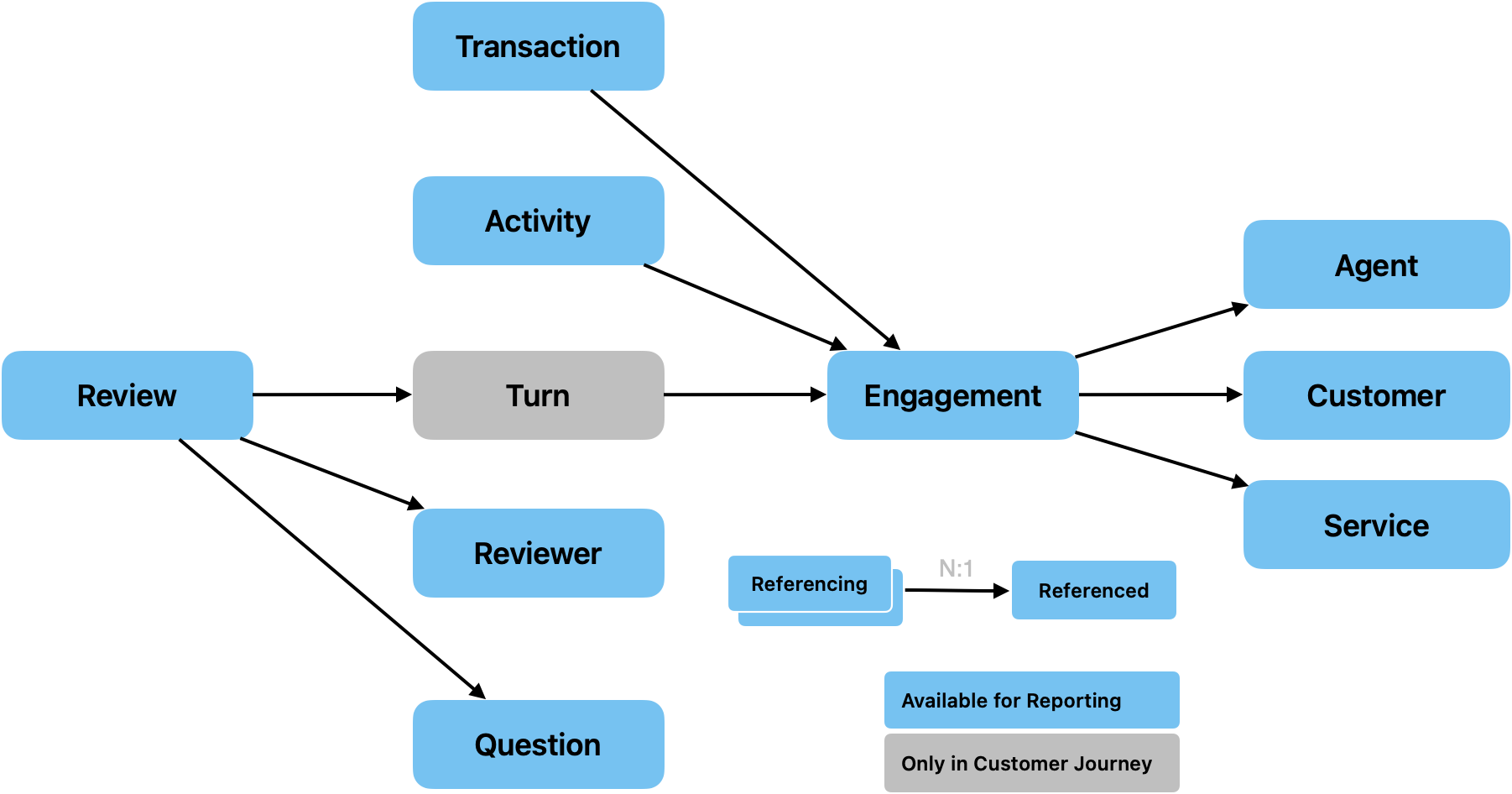
Each data set has a set of attributes, facts, and references to related data sets.
| Entity | Description |
|---|---|
| Activity | Detailed break down of agent load and activity. |
| Agent | The person or a service that interacts with customers on behalf of the company. Each engagement is associated with one agent. |
| Customer | The person that the company engages with during the conversation. We recommend that all engagements in a single conversation be associated with a single customer although it is technically possible to have conversation where multiple customers are involved. |
| Engagement | Individual engagements between agents and customers. Multiple engagements can be grouped into one conversation. |
| External Agent | Person or an organization outside of your company that can engage with the customers in the conversations. |
| Question | Question that was answered in a review. |
| Review | Review represents individual responses, comments and tags associated with Engagements. Reviews contain feedback from customers, agents, reviewers and automatic reviews. |
| Reviewer | Person or a service that provides Reviews for Engagements. |
| Service | Service (or product) primarily associated with the conversation. This dataset enables you to attribute conversations to specific, products and eventually partners on whose behalf you engage in conversations with customer. |
| Transaction | Transactions that happened during this engagements. Transactions can have associated revenue and costs to enable reporting on financial aspects of the engagements. There can be multiple transactions for a single Engagement. |
| Turn | Granular breakdown of individual engagements. Turns represent different events in different types of engagements. In messaging they represent a single message sent by a participant, in voice conversation, they represent a single talk by one of the participants, in menu engagements they represent individual menu steps, etc. Turns are not available for reporting. They are visible in the customer journey. |
Attributes
An Attribute is a property of a Data Set that can be used for segmentation and filtering of data visible in the reports and dashboards.
Enumerations
Enumerations are special types of attributes that can contain only values allowed by Salted CX. Unsupported values cause the data to fail to load using our Ingest API.
Entities
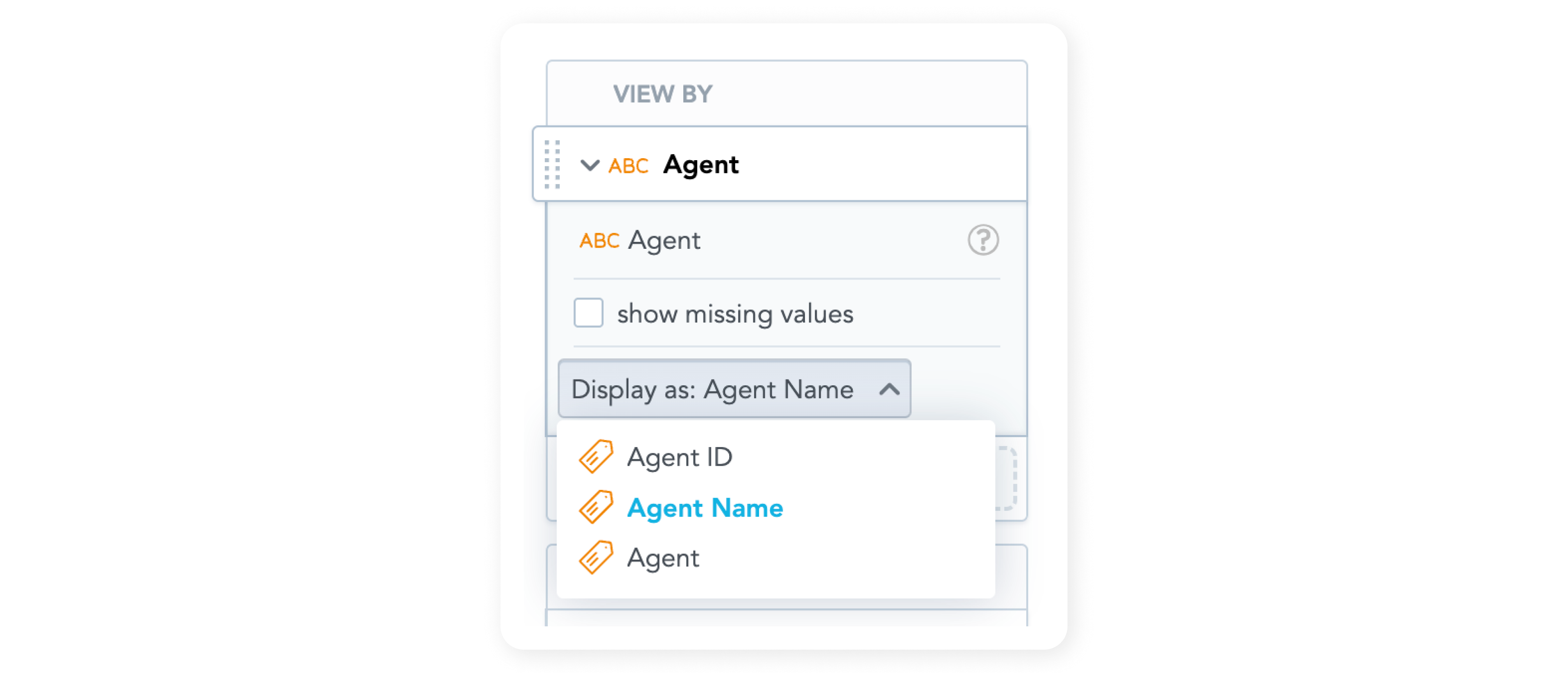
Entities are very simple Data Sets. Unlike Data Sets, they have only one attribute with two labels and no facts. Every entity has the same set of one attribute and two labels for that attribute.
| Property | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| <Entity Name> | PID | Permanent identifier generated by Salted CX and uniquely identified the item. The PID cannot be changed after the entity is created. |
| <Entity Name> ID | Label for <Entity Name> | ID that the entity has in a third-party system. Salted CX does not enforce any format for the ID. The ID has to fit into 100 characters as attributes have to. |
| <Entity Name> Name | Label for <Entity Name> | Name that is the default representation of the entity in the user interface. The name should be easy for users to read and understand. The name is also limited to 100 characters. |
Entities enable you to have a unique representation of important items in the contact center, with a human-friendly visualization. Entities also enable you to easily rename the items without breaking relationships between important data points.
PID
Each item in a dataset and every entity has a unique Permanent Identifier (PID). PID is a special type of attribute. PID is always a UUID that is either generated randomly or deterministically based on identifiers in the connected platform. Once a PID is generated for an item, it cannot be changed in the future.
Labels
Labels are alternative visualizations for attributes. While you might use a hard-to-read value that you are certain is unique as an attribute value, the unique value may be very inconvenient for end users to read.
There might be two items with the same label but different underlying attribute values. If such a label is used in insights, you will see two different segments with the same name and different metric values.
Facts
A Fact is a numeric value in the Logical Model. Facts can be used for arithmetic operations, aggregated, and ultimately form the foundation for creating metrics.
Metrics cannot be used for filtering in insights and dashboards. However, you can use fact values in metric filtering conditions.
Date, Time, and Duration
All dates and times in the logical model have one-minute granularity. There are multiple dates and times in the Logical Model.
All durations in the logical model are in seconds.
Technical items in data sets
Some data sets have technical values. Technical values have an attribute Type set to value Technical. You can use this attribute to filter the technical items in the data sets.
Technical items are stored by default in the Agent, Customer, and Engagement data sets.
Data not in logical model
The logical model does not contain the following data:
- Conversation content, such as transcripts or voice recordings. It may, however, contain metadata extracted from the content, such as discussed topics, sentiment, and other features extracted from the content. The content is stored separately and displayed only when users drill down to the customer journey and have permission to view the conversation content.
- Customer's personally identifiable data. Customer's personally identifiable data is removed and replaced by identifiers from the customer profile. We do not expose personally identifiable information in analytics or in the customer journey. To display personal identifiable information, the user must have a dedicated permission and click on a specific masked value to view it.